Python3 列表
序列是 Python 中最基本的数据结构。
序列中的每个值都有对应的位置值,称之为索引,第一个索引是 0,第二个索引是 1,依此类推。
Python 有 6 个序列的内置类型,但最常见的是列表和元组。
列表都可以进行的操作包括索引,切片,加,乘,检查成员。
此外,Python 已经内置确定序列的长度以及确定最大和最小的元素的方法。
列表是最常用的 Python 数据类型,它可以作为一个方括号内的逗号分隔值出现。
列表的数据项不需要具有相同的类型
创建一个列表,只要把逗号分隔的不同的数据项使用方括号括起来即可。如下所示:
list1 = ['Google', 'Runoob', 1997, 2000] list2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ] list3 = ["a", "b", "c", "d"] list4 = ['red', 'green', 'blue', 'yellow', 'white', 'black']
访问列表中的值
与字符串的索引一样,列表索引从 0 开始,第二个索引是 1,依此类推。
通过索引列表可以进行截取、组合等操作。
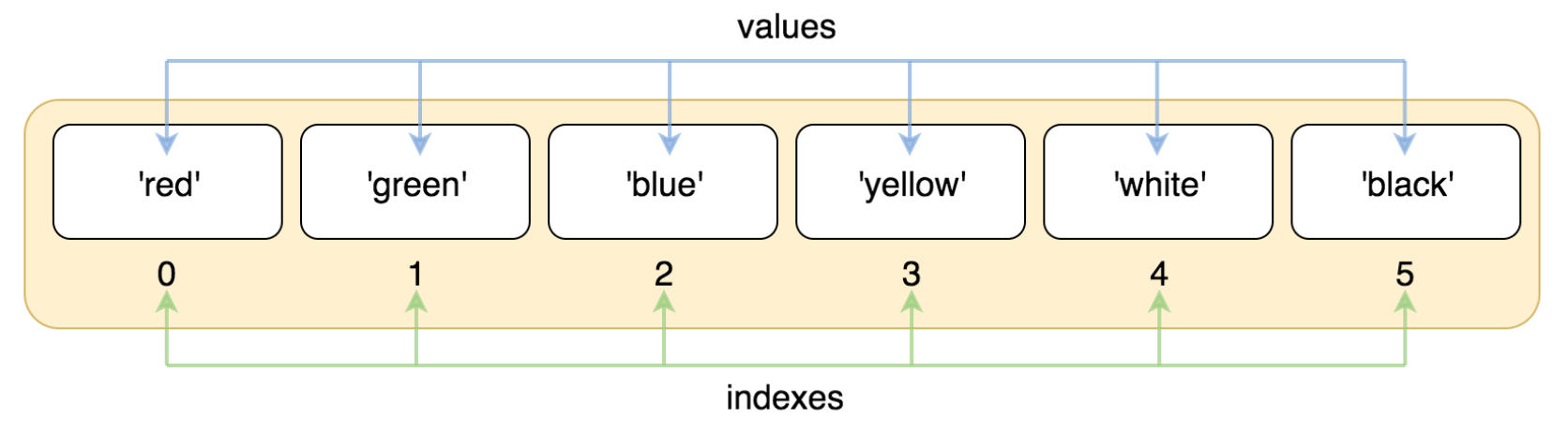
#!/usr/bin/python3 list = ['red', 'green', 'blue', 'yellow', 'white', 'black'] print( list[0] ) print( list[1] ) print( list[2] )
以上实例输出结果:
red green blue
索引也可以从尾部开始,最后一个元素的索引为 -1,往前一位为 -2,以此类推。
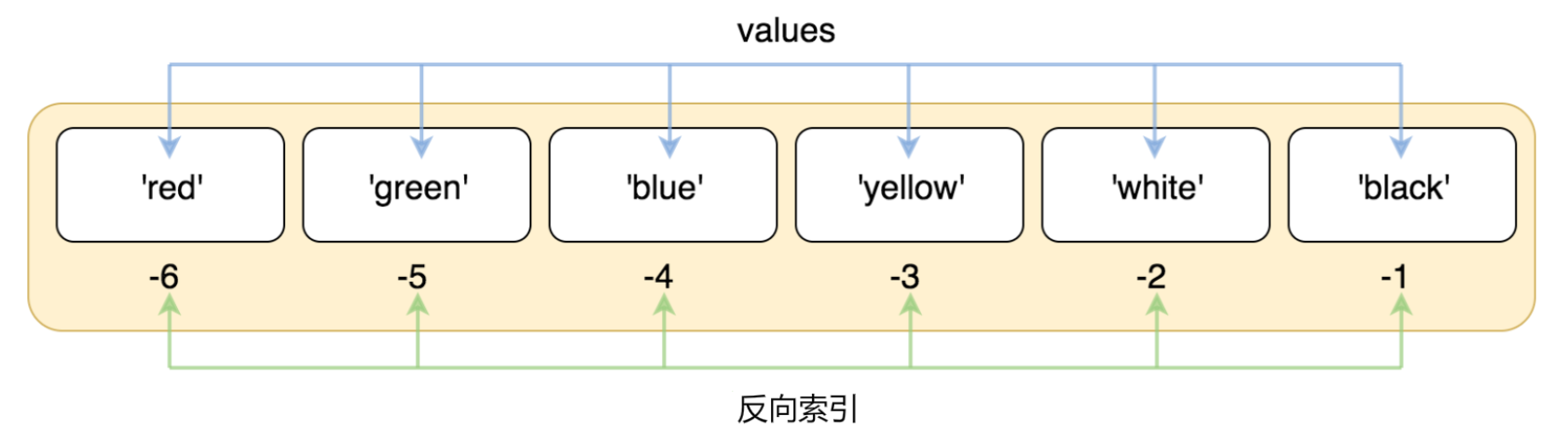
#!/usr/bin/python3 list = ['red', 'green', 'blue', 'yellow', 'white', 'black'] print( list[-1] ) print( list[-2] ) print( list[-3] )
以上实例输出结果:
black white yellow
使用下标索引来访问列表中的值,同样你也可以使用方括号 [] 的形式截取字符,如下所示:
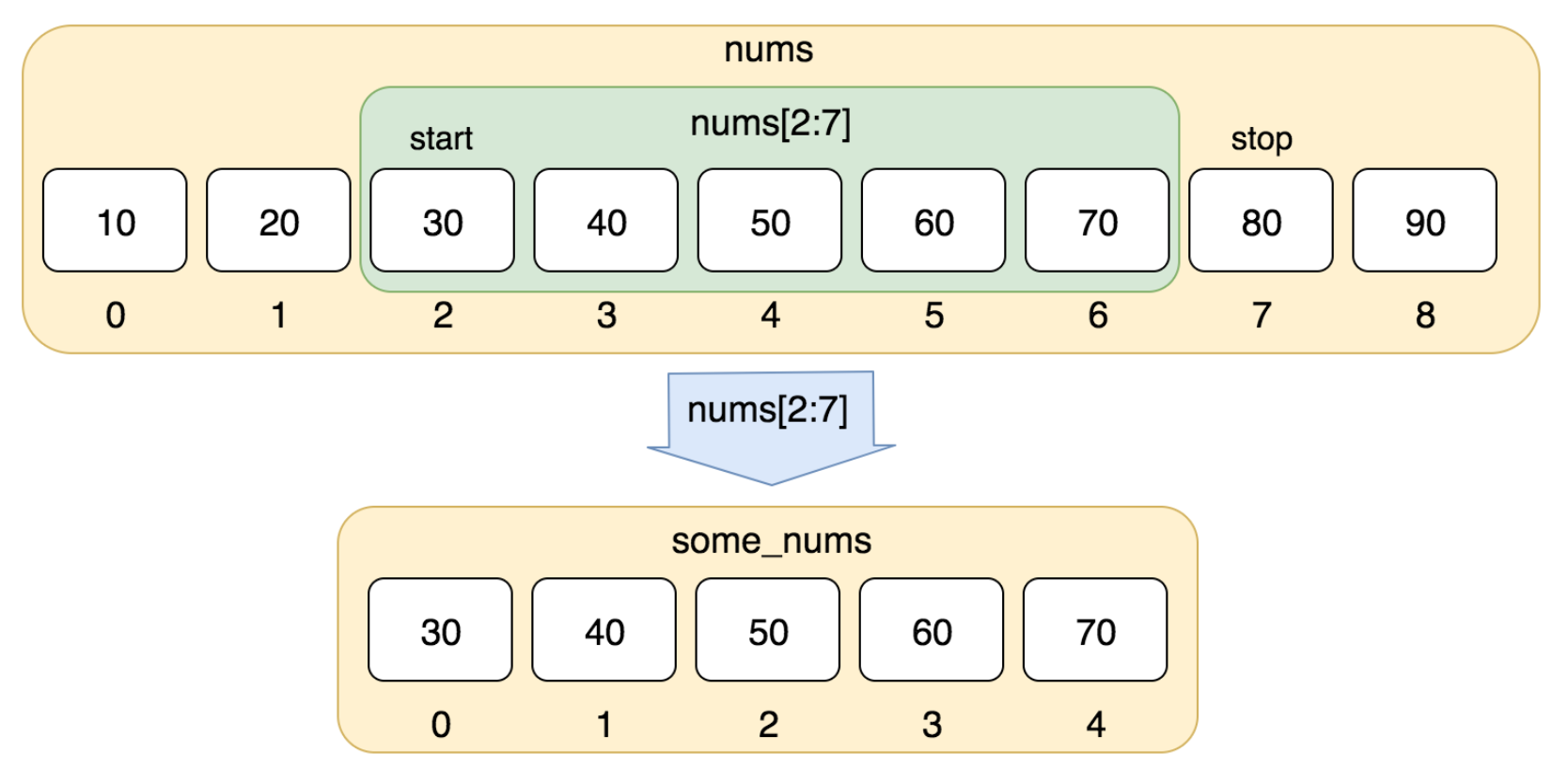
#!/usr/bin/python3 nums = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90] print(nums[0:4])
以上实例输出结果:
[10, 20, 30, 40]
使用负数索引值截取:
#!/usr/bin/python3
list = ['Google', 'Runoob', "Zhihu", "Taobao", "Wiki"]
# 读取第二位
print ("list[1]: ", list[1])
# 从第二位开始(包含)截取到倒数第二位(不包含)
print ("list[1:-2]: ", list[1:-2])以上实例输出结果:
list[1]: Runoob list[1:-2]: ['Runoob', 'Zhihu']
本文未完全显示,开通会员查看全文......